Vector Databases & Embeddings
Master vector databases and embeddings to build intelligent search, retrieval, and AI memory systems. Price Match Guarantee
Full Lifetime Access
Access on any Device
Technical Support
Secure Checkout
Course Completion Certificate
Price Match Guarantee
Full Lifetime Access
Access on any Device
Technical Support
Secure Checkout
Course Completion Certificate
 90% Started a new career
BUY THIS COURSE (
90% Started a new career
BUY THIS COURSE (GBP 12 GBP 29 )-
 82% Got a pay increase and promotion
82% Got a pay increase and promotion
Students also bought -
-
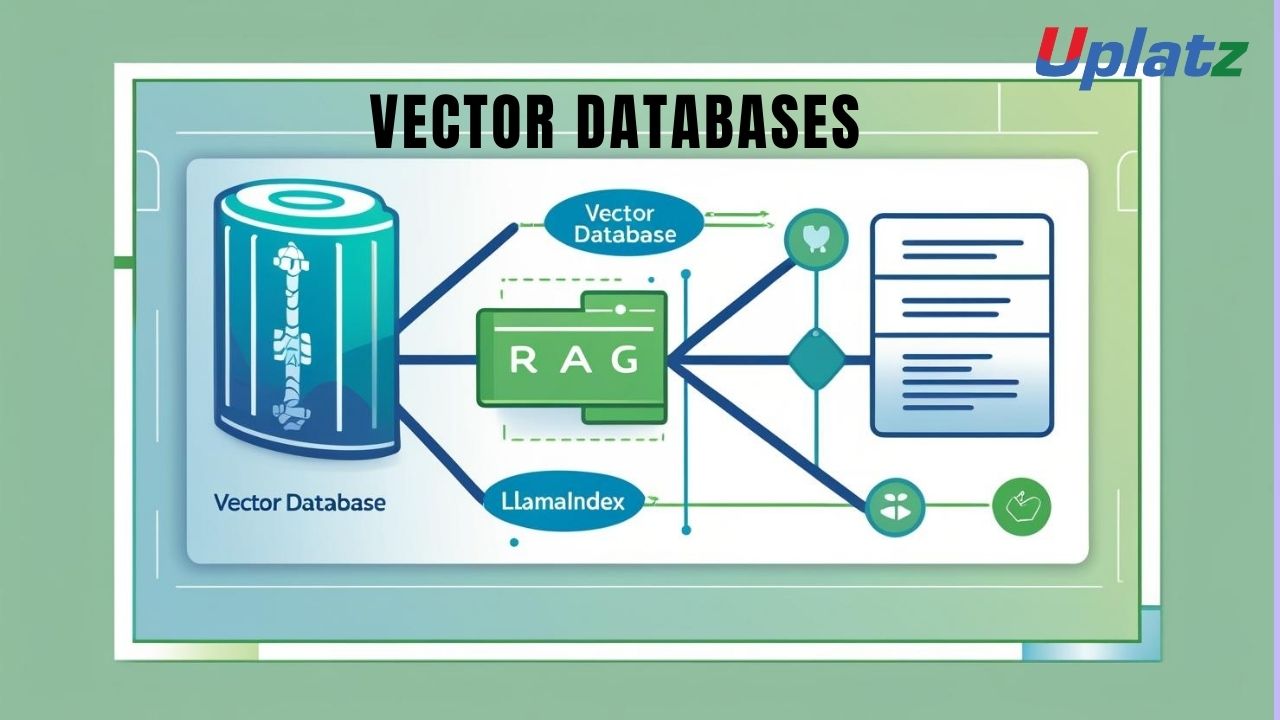
- Vector Databases & RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) with LlamaIndex
- 10 Hours
- GBP 29
- 10 Learners
-

- SQL Programming with Microsoft SQL Server
- 55 Hours
- GBP 29
- 5739 Learners
-

- MongoDB
- 15 Hours
- GBP 12
- 259 Learners

The world of artificial intelligence is moving beyond keywords — into understanding meaning, context, and relationships between ideas. At the core of this evolution are vector databases and embeddings — the invisible engines that enable semantic search, intelligent chatbots, and memory-aware large language models (LLMs).
This course, Vector Databases & Embeddings – Powering Semantic Search and AI Intelligence, is a complete, hands-on journey into how modern AI systems represent and retrieve meaning. It combines deep theoretical understanding with practical, industry-relevant implementation skills that every AI engineer and data scientist needs today.
🔍 What Are Vector Databases and Embeddings?
Embeddings are numerical representations of meaning — they transform words, sentences, images, or any data type into high-dimensional vectors that encode semantic relationships. Two similar concepts will have vectors that are close together in this multi-dimensional space, allowing machines to understand context rather than just literal text.
A vector database, on the other hand, is a specialized data system designed to store, index, and query these embeddings efficiently. It uses similarity search algorithms to retrieve the most relevant information based on meaning — not on exact keyword matches. This is the backbone of intelligent systems like semantic search engines, recommendation systems, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines for LLMs.
⚙️ How Do Vector Databases and Embeddings Work?
Traditional databases rely on structured data and exact matches. In contrast, vector databases use Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) algorithms such as HNSW, IVF, and PQ to find the most similar vectors within milliseconds — even in massive datasets.
The process typically involves:
-
Generating embeddings using deep learning models such as OpenAI’s embedding APIs, BERT, or Sentence Transformers.
-
Storing the embeddings in a vector database such as Pinecone, FAISS, Chroma, or Weaviate.
-
Querying by converting a user’s question or document into a new embedding vector and comparing it against existing ones to find the most semantically similar results.
This allows AI systems to understand that “How to fix a car engine” and “Car repair guide” are semantically related — even though they share few common words.
🏭 How Vector Databases Are Used in the Industry
Vector databases are redefining how modern companies manage and retrieve knowledge. Industry giants like Google, Meta, OpenAI, Microsoft, and Spotify employ embedding-based systems to deliver more relevant, personalized, and intelligent user experiences.
Here are some real-world use cases:
-
Semantic Search Engines: Search results ranked by meaning, not by keywords.
-
Chatbots & LLMs: Context retention and long-term conversational memory.
-
E-Commerce: Recommendation systems suggesting products based on contextual similarity.
-
Healthcare: Medical literature retrieval for precise diagnosis support.
-
Enterprise Knowledge Management: Contextual document discovery and internal AI assistants.
By learning to build such systems, you’ll gain the skills that power applications like ChatGPT’s memory, Notion AI’s document retrieval, or Spotify’s recommendation engine.
🌟 Benefits of Learning Vector Databases & Embeddings
Mastering vector databases and embeddings gives you a strategic advantage in AI development, data science, and applied machine learning. Key benefits include:
-
Understand the Language of Meaning: Move beyond keyword search to systems that truly comprehend human intent.
-
Build Smarter AI Applications: Power RAG pipelines, AI chatbots, recommendation engines, and contextual assistants.
-
Bridge AI and Data Engineering: Integrate LLM capabilities directly into database and analytics workflows.
-
High-Value Career Growth: Skills in embeddings, FAISS, Pinecone, and LangChain are among the most in-demand in the AI job market.
-
Enterprise-Ready Expertise: Learn to design scalable pipelines that combine performance, accuracy, and contextual reasoning.
These competencies position you at the forefront of AI innovation — where data, meaning, and intelligence converge.
📘 About This Course
This comprehensive course takes you step-by-step through the conceptual, mathematical, and practical aspects of vector databases and embeddings. It blends deep learning theory with real-world implementation, ensuring you understand both the why and how behind every concept.
You will learn:
-
How embeddings represent meaning in high-dimensional vector space.
-
How to generate and fine-tune embeddings using pre-trained or custom models.
-
How to store, index, and query embeddings efficiently using Pinecone, FAISS, Chroma, and Weaviate.
-
How to implement semantic search, RAG pipelines, and memory-augmented chatbots.
-
How to integrate embeddings into frameworks like LangChain and OpenAI APIs for intelligent applications.
Each concept is reinforced through guided projects, assignments, and real-world coding exercises, helping you gain both practical proficiency and conceptual clarity.
💡 What You’ll Build
Throughout the course, you’ll work on multiple mini-projects and end-to-end implementations such as:
-
A semantic document retrieval engine using embeddings and FAISS.
-
A context-aware chatbot powered by a vector memory store.
-
A RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) system integrating OpenAI models with Pinecone.
-
A vector visualization dashboard to explore high-dimensional similarity.
By completing these projects, you’ll graduate with a professional portfolio that demonstrates real-world capability in embedding-based AI systems.
👩💻 Who Should Take This Course
This course is tailored for a broad range of professionals and learners:
-
AI Engineers and Data Scientists building intelligent retrieval and RAG systems.
-
Machine Learning Developers implementing embeddings for contextual reasoning.
-
Database Engineers and Architects exploring next-generation data storage.
-
Researchers and Students delving into semantic representation and vector learning.
-
Tech Enthusiasts curious about how ChatGPT and other AI systems store and recall knowledge.
No prior experience in vector mathematics is required — the course explains all core concepts with visual and code-based examples.
🧩 Course Format and Learning Experience
This self-paced program combines structured learning with hands-on experimentation.
Each module includes:
-
HD video tutorials with live demonstrations.
-
Downloadable Jupyter notebooks and datasets.
-
Quizzes and checkpoint assessments.
-
Discussion of architecture and scaling patterns.
-
End-of-module projects for applied understanding.
You’ll also receive lifetime access to all course materials, including continuous updates as vector search and embedding technologies evolve.
🌐 Why Choose This Course
-
Comprehensive Curriculum: Covers theory, math intuition, and system design.
-
Practical Application: Focus on implementation using real-world tools and APIs.
-
Industry Relevance: Aligned with cutting-edge AI workflows like LangChain and RAG.
-
Career Growth: Equips you with in-demand, high-paying AI skills.
-
Future-Ready Learning: Stay ahead in the shift toward semantic, context-driven AI systems.
🚀 Final Takeaway
Vector databases and embeddings are transforming how artificial intelligence interacts with data. They enable machines to think contextually — a key step toward genuine understanding.
By mastering this technology, you’ll be prepared to design AI systems that understand, remember, and reason — the core capabilities driving the next generation of intelligent applications.
This course is your pathway to building smarter search engines, memory-based assistants, and enterprise AI pipelines that go beyond keywords — into meaning, context, and intelligence.
By completing this course, learners will be able to:
- Understand the fundamentals of embeddings and vector similarity.
- Create, evaluate, and store vector representations of text, images, and data.
- Use vector databases for semantic search and retrieval.
- Integrate vector systems into AI pipelines like RAG and conversational memory.
- Optimize indexing, scaling, and latency in vector queries.
- Deploy and monitor vector-powered AI systems in production environments.
Course Syllabus
Module 1: Introduction to Embeddings and Vector Databases
Concepts of vectorization, semantic similarity, and vector storage fundamentals.
Module 2: Understanding Embeddings
How embeddings encode meaning; word2vec, GloVe, Sentence-BERT, and OpenAI embeddings.
Module 3: Generating and Using Embeddings
Creating embeddings for text, image, and structured data using popular APIs and models.
Module 4: Vector Similarity and Distance Metrics
Cosine similarity, Euclidean distance, inner product, and their applications in retrieval.
Module 5: Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) Search
Concepts, trade-offs, and algorithms like HNSW, IVF, and PQ for scalable similarity search.
Module 6: Introduction to Vector Databases
Overview of Pinecone, FAISS, Weaviate, Qdrant, and Chroma with use case comparisons.
Module 7: Data Indexing and Retrieval Workflows
Index construction, updates, metadata filters, and hybrid search techniques.
Module 8: Integration with LLMs and RAG Pipelines
Connecting embeddings to retrieval-augmented generation for context-based AI.
Module 9: Building Memory-Enhanced Chatbots
Implementing persistent memory in conversational agents using vector stores.
Module 10: Scaling and Optimization
Techniques for query efficiency, load balancing, and distributed vector storage.
Module 11: Evaluation and Monitoring
Evaluating embedding quality, retrieval accuracy, and drift management.
Module 12: Capstone Project – Semantic Retrieval System
Design and deploy a complete semantic search system using FAISS or Pinecone integrated with an LLM for contextual responses.
Upon successful completion, learners will receive a Certificate of Specialization in Vector Databases & Embeddings from Uplatz.
This certification validates your practical ability to build, optimize, and deploy embedding-powered systems that form the foundation of next-generation AI and search technology.
Proficiency in vector databases and embeddings opens high-demand roles such as:
- AI Infrastructure Engineer
- Data Retrieval Engineer
- RAG Pipeline Developer
- Semantic Search Engineer
- Machine Learning Engineer (NLP/CV)
- Vector Database Specialist
These skills are crucial for organizations working in generative AI, search engines, recommendation systems, and enterprise AI architecture — making this specialization one of the most sought-after technical domains in 2025 and beyond.
What are embeddings in AI and why are they important?
Embeddings are dense vector representations of data that capture semantic meaning, allowing AI systems to perform similarity searches and contextual reasoning.
How does a vector database differ from a traditional database?
A vector database stores high-dimensional numerical representations (vectors) instead of discrete fields, enabling semantic and similarity-based querying rather than exact matching.
What is cosine similarity and why is it used in vector search?
Cosine similarity measures the angle between two vectors, determining how similar their directions are — ideal for comparing semantic closeness in embeddings.
What are common algorithms used for Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) search?
HNSW, IVF (Inverted File Index), and PQ (Product Quantization) are widely used ANN algorithms for fast and scalable similarity search.
Name a few popular vector databases used in AI applications.
Pinecone, FAISS, Weaviate, Qdrant, Milvus, and Chroma are among the most popular vector databases today.
How are embeddings integrated into RAG pipelines?
Embeddings enable context retrieval by finding semantically relevant data chunks, which are then used by LLMs during response generation.
What are hybrid search techniques?
Hybrid search combines keyword-based (symbolic) and vector-based (semantic) retrieval for improved accuracy and contextual relevance.
What challenges arise in maintaining large-scale vector databases?
Challenges include handling dimensionality, ensuring low-latency queries, managing updates, and optimizing storage for billions of vectors.
How can embedding quality be evaluated?
Using metrics like cosine similarity thresholds, retrieval accuracy, and task-based evaluations (e.g., semantic search precision).
What are real-world applications of vector databases and embeddings?
They power search engines, chatbots, recommendation systems, fraud detection, document retrieval, and contextual AI assistants.









