Unix and Linux File Utilities
Learn about Unix OS and about its basic commands, also learn some important Unix utilities that can be used in our day-to-day life. View Course Curriculum
Price Match Guarantee
Full Lifetime Access
Access on any Device
Technical Support
Secure Checkout
Course Completion Certificate
View Course Curriculum
Price Match Guarantee
Full Lifetime Access
Access on any Device
Technical Support
Secure Checkout
Course Completion Certificate
 41% Started a new career
BUY THIS COURSE (GBP 29)
41% Started a new career
BUY THIS COURSE (GBP 29)
-
 71% Got a pay increase and promotion
71% Got a pay increase and promotion
Students also bought -
-
- Unix - Linux - Shell Scripting
- 25 Hours
- GBP 29
- 347 Learners
-
- Unix and Shell Programming
- 5 Hours
- GBP 29
- 111 Learners
-

- Talend
- 20 Hours
- GBP 29
- 117 Learners

Linux provides basic and advanced concepts of Linux. It is designed for beginners and professionals. Unix is also operating system like Linux. It is a commercial OS.
Unix software usually focuses on how the computer infrastructure (including the computer hardware, operating system, application software and data storage) operates. Application software could be thought of as anything that could run the same way on any operating system.
Unix is a Computer Operating System which is capable of handling activities from multiple users at the same time. Unix systems also have a graphical user interface (GUI) similar to Microsoft Windows which provides an easy to use environment. The UNIX operating system is made up of three parts; the kernel, the shell and the programs.
There are 10 useful Utility tools for Linux users which include various network monitoring and system auditing.
1. W - Display who is logged into the system and what process executed by them.
2. Nmon–Nmon or nigel’s monitor is a tool which displays performance information of the systems.
3. Ncdu – A command utility is a cursor based version of ‘du’ the command is used to analyze disk space occupied by various directories.
4. Slurm – A command-line utility used for command based network interface bandwidth monitoring, it will display asci based graphic.
5. Findmnt – Findmnt command is used to find mount file system. It is used to list mount devices and can also mount or unmount devices as and when required it comes as part of util-linux.
6. dstat – Combined and flexible tool can be used to monitor memory, process, network or disk space performance.
7. saidar – Another cli based system statistics monitoring tool, provide information about disk uses, network, memory swap etc.
8. SS or socket statistics is a good alternative to netstat it directory gather information from kernel space nad play fast in comparison to the netstat utility.
9. Ccze – A tool that decorate your logs.
10. Ranwhen.py – A python-based terminal utility that can be used to display system activities graphically.
There are three basic types of files
Ordinary Files − An ordinary file is a file on the system that contains data, text, or program instructions.
Directories − Directories store both special and ordinary files. For users familiar with Windows or Mac OS.
Special Files − Some special files provide access to hardware such as hard drives, CD-ROM drives, modems, and Ethernet adapters.
The Unix and Linux File Utilities by Uplatz is a complete end-to-end course covering all topics.
Course/Topic - Unix and Linux File Utilities - all lectures
-
In this session we will discuss about standard I/O, redirection and pipes, we will also discuss about the meta characters.
-
In this session we will discuss about changing file access rights (uses and permission including both symbolic and absolutemodes)
-
In this session we will discuss about soft links and hard links we will also learn how to check file integrity.
• Learn to build and use UNIX/Linux tools and utilities
• Perform complex search strings using regular expressions
• Explore extended regular expressions with grep, sed, and awk
• Understand how to implement microservices using Spring Cloud.
• Learn end-to-end knowledge of Unix/Linux systems, administration
• Learn Linux Basic Commands.
• Learn history, open source licences, various Linux distributions and Linux installation
• Employ text filters to manipulate text and data
Unix and Linux File Utilities - course syllabus
· Standard I/O, redirection and pipes
· File descriptors and its related usage of metacharacters (>, >>, <, <<, <<<)
· Changing file access rights (users and permissions including both Symbolic and Absolute modes) (chmod)
· Soft links and hard links
· Checking file integrity
The Unix and Linux File Utilities Certification ensures you know planning, production and measurement techniques needed to stand out from the competition.
The utilities, on the other hand, reside on the computer's disk and are only brought into memory as requested. Virtually every command you know under the Unix system is classified as a utility; therefore, the program resides on the disk and is brought into memory only when you request that the command be executed.
The shell utilities implement a number of shell commands you can use interactively or in shell scripts. Each utility program performs a specific task. The idea is that you can combine these commands in shell scripts to perform more complicated tasks.
Linux refers to the kernel of the GNU/Linux operating system. More generally, it refers to the family of derived distributions. Unix refers to the original operating system developed by AT&T. More generally, it refers to a family of derived operating systems. Original code developed by Linus and the GNU Foundation.
All data in Unix is organized into files. All files are organized into directories. These directories are organized into a tree-like structure called the filesystem. When you work with Unix, one way or another, you spend most of your time working with files.
Uplatz online training guarantees the participants to successfully go through the Unix and Linux File UtilitiesCertification provided by Uplatz. Uplatz provides appropriate teaching and expertise training to equip the participants for implementing the learnt concepts in an organization.
Course Completion Certificate will be awarded by Uplatz upon successful completion of the Unix and Linux File Utilities Online course.
The Unix and Linux File Utilities Draws an average salary of $134,000 per year depending on their knowledge and hands-on experience.
Unix is in great demand in the area of software technology with different career paths like an engineer in Unix, an administrator in Unix, Systems engineer in Unix, Infrastructure administrator in Unix, Analyst Engineer in Unix, Production support engineer in Unix, Engineer in Linux, Admin in Linux, etc.
Minimum qualifications for this job typically include a bachelor's degree in information technology (IT), computer engineering, computer science, network and system administration, or another relevant subject. Senior roles require several years of on-the-job experience with Unix.
Note that salaries are generally higher at large companies rather than small ones. Your salary will also differ based on the market you work in.
SR, Unix engineer.
Unix operation engineer.
Unix system admin.
Q 1) What is the description of Kernel?
Answer: Kernel is the master program that controls the resources of the computer. The resource allocation to different users and tasks is handled by this section. The kernel does not communicate directly with the user and instead, it starts separate interactive program call shell to each user when logged in to the system.
Q 2) What is a single-user system?
Answer: A single-user system is a personal computer with an operating system, designed to operate by a single user at a given time. These systems become more popular since low-cost hardware and availability of a wide range of software to perform different tasks.
Q 3) What are the main features of UNIX?
Answer: Main features of UNIX are as follows:
- Machine independent
- Portability
- Multi-user operations
- Unix Shells
- Hierarchical file system
- Pipes and filters
- Background processors
- Utilities
- Development tools.
Q 4) What is called Shell?
Answer: The interface between the user and the system is called the shell. Shell accepts commands and set them to execute for user operations.
Q 5) What are the responsibilities of a shell?
Answer: Responsibilities of a shell can be enlisted as:
- Program execution
- Input/output redirection
- Filename and variable substitution
- Pipeline hookup
- Environment control
- Integrated programming language
Q 6) What is the general format of UNIX command syntax?
Answer: In general consideration, UNIX shell commands follow the below pattern:
Command (-argument) (-argument) (-argument) (filename)
Q 7) Describe the usage and functionality of the command “rm –r *” in UNIX?
Answer: The command “rm –r *” is a single line command to erase all files in a directory with its subdirectories.
- “rm” – command for deleting files.
- “-r” – command to delete directories and subdirectories with files within.
- “*” – indicates all entries.
Q 8) Describe the term directory in UNIX?
Answer: A specialized form of a file that maintains the list of all files included in it, is called a directory. Each file is assigned to a directory.
Q 9) Specify the difference between absolute path and related path?
Answer: Absolute path refers to the exact path as defined from the root directory. Related path refers to the path related to the current location.
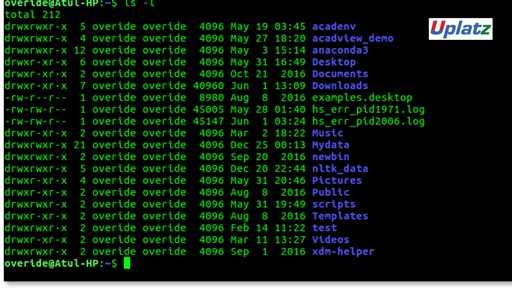
Q 10) What is the UNIX command to list files/folders in alphabetical order?
Answer: The ‘ls –l’ command is used to list down files and folders in alphabetical order. When you use ‘ls –lt’ command, it lists down files /folders sorted with modified time.









